

This reaction is normal but here may bigger,
A essay of schematisation of the chemic shapes:
Ion : a atom or molecule won or lost one or many electrons, we can see two categories :
Anion : a atom or molecule lost one or many electrons, so it's negative.
Cation : a atom or molecule won one or many electrons, so it's positive.
It need catalyst for that oxygen to create a reactions with organical mater this catalists are a big enzymes
when a atom lost a electron we speak of redox reaction.
- A oxydase is a enzyme catalyst a reaction of oxydo-réduction so this reaction use a dioxygen molecule (O2)
as acceptor electron.
The mitochondria is divided in 5 parts writted in roman numnbers : I,II,III,IV,V,
each part fabrique is a chemic reaction to creat in part V energy or a molecule of ATP, it's explained below
In -- the compartment I-- there is the reaction following :
the gen MnSOD mitochondrial create isoenzyme SOD2 in part I of mitochondrie so the reaction following :
O2-.
NDAPH+H+ give NAD+ and export H+↑
H+ = ion hydronium so lost is electron (or called proton hydrogen).
NADP = nicotinamide adénine dinucléotide is a coenzyme oxydo-reduction.
NADPH or NADPH2 or NADPH+H+ mechanism against oxydative stress.
NADPH+H+ is used for biosynthese of fat acids of cholesterol
SOD2 = Superoxide dismutase 2
O 2-.= anion superoxyde
In the compartment II there is reaction following :
FADH2 → FAD
FAD = Flavine adénine dinucléotide ( protein that contain flavine transportor of electrons, create by vitamine B2 ).
in the compartiment III there is reaction following :
this era III (paroi intermédiaire) of mitochondria product
O2-., via SOD1. exportation of H+ ↑
SOD1 =
O2-. = anion superoxyde (discovered in 1968) anion superoxyde interact with ions H+ ( because there is won a electron of him and so H lost 1 electron so H become a proton alone.
In compartment IV there is reaction following :
1/O2+2H-->H2O + export de H+ (so a oxydase process) H2O = water O2 = dioxigène or oxygen
In compartment V there is reaction following :
ATP ↓ - ADP+Pi
Pi = inorganic phosphate
ADP = adénosine diphosphate is a nucléotide
inside the membrane of mitochondria there is the reaction following :
O2.→SOD1→H2O2↑
anion superoxyde = O2.-
SuperOxydes Dismutases 1 = SOD (a enzyme antioxydante)
H2O2 hydrogen peroxide
remark de l'étude : SOD1 and SOD2 have studied on mice, it exist SOD3 too
- So the cytosolic enzyme CuZnSOD by catalisat(?) give a reaction of anions superoxyde
In mitochondria there si a reaction by a molecule called catalase ( or CAT ) water from peroxyde hydrogen as this : H2O2 →CAT→H2O ↓ And when the catalase down it's dangerous because peroxyde hydrogène H2O2,
overwhelm catalase mitochondrial and catalase of peroxysome. peroxyde hydrogen give a reaction with iron ions called Fenton reaction
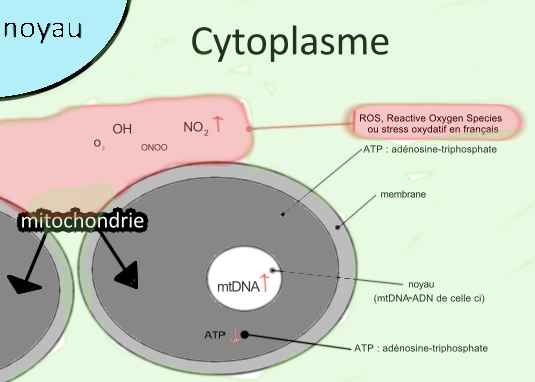
Thz mitochondrial network create many ROS (reactive oxydatif species) so too stress oxydatif :
this are Ros :
O2-.= anion superoxyde
OH- = anion hydroxyde
CO3.- = anion carbonate
NO2- = dioxyde d'azote
ONOO- = ion peroxynitrite
To summary : so we are two way to moment :
1- what are molecules destroyed by ROS ^per organes.
2- how to create a depletion of ros in some organes with nor risks for patients.
then there was some researchs :
before, we saw reaction of fth1 and aptx on DNA,
on Cortisol on few next chapters.,
on glucose don't transform enough ATP, the need of ATP by cell in a another chapter,
on glutathion reductase(GSR) in a another chapter too.
